Research
Functional and Quantitative Breast Tomosynthesis
Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT), see Fig. 1-2, has rapidly been introduced for clinical use as an adjunct or replacement of mammography. Currently, most hospitals in the Netherlands use DBT for detection and diagnosis of breast cancer, see Fig. (1). This is also the case in the rest of Europe and North America.
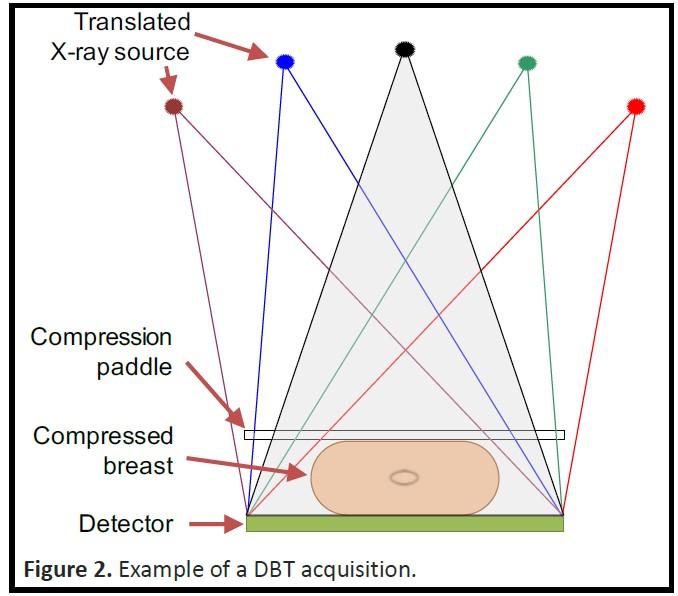
Figure 1: Schematic of the DBT acquisitions setup.
Figure 2: Image of the tomosynthesis device Mammomat Inspiration, Siemens.
However, once the cancer is diagnosed, functional information about the tumor, as opposed to anatomical information such as its shape and extent as obtained with DBT, is needed to optimize and monitor treatment. In this project, we are working on extending the capabilities of tomosynthesis to create a new functional imaging modality: 1) dual-energy DBT (DE-DBT) for the distinction between cysts from solid lesions at screening, without contrast injection nor increase in the radiation dose; and 2) quantitative dynamic contrast-enhanced (QDCE)-DBT. The former would results in the reduction of recalls of healthy women for additional testing. And the latter method will help us obtain a complete characterization of tumor status before and throughout treatment, which may improve local and systemic therapy planning, response monitoring, and outcome prediction, reducing current breast cancer morbidity and mortality. The creation of QDCE-DBT will involve the development, optimization, and testing of novel DBT image acquisition techniques and of spectral reconstruction, deep learning-based image quantification, and motion correction algorithms.
Objectives of the project can be seen in Fig. 3 and the steps are described in the following manner:
i. develop and optimize the required image acquisition methods for QDCE-DBT.
ii. improve the dual-spectrum reconstruction algorithm for use in QDCE-DBT.
iii. develop deep learning-based methods for quantitative accuracy in QDCE-DBT.
iv. adapt these methods for cyst vs. solid mass characterization with DE-DBT.

Figure 3: the improject involves four work packages (WPs) corresponding to the four objectives listed above. Three WPs will result in QDCE-DBT for treatment personalization and monitoring, and one WP will develop DE-DBT for cyst vs. mass discrimination at screening.
In more detail, the step are the following
i) Development and Optimization of QDCE-DBT Acquisition Methods
This section focuses on developing and optimizing Quantitative Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (QDCE-DBT) acquisition techniques, in collaboration with Siemens. This includes the following tasks:
Task 1.1 – Digital Phantoms:
Enhance existing digital dynamic breast phantoms by incorporating simulated mechanical compression using NiftySim. These models will be validated against patient data and used to optimize QDCE-DBT acquisition parameters.
Task 1.2 – Physical Phantoms:
Design and build a physical dynamic breast phantom with a contrast flow module, in collaboration with Sun Nuclear. It will combine a perfusion system with a 3D-printed anthropomorphic breast phantom for real-world testing of acquisition methods and algorithms.
Task 1.3 – Acquisition Optimization:
Adapt existing DBT simulations to reflect Siemens' system. Validate simulations, optimize x-ray parameters (tube voltages, filtration, dose), and test using both digital and physical phantoms. Emphasis is on accurate material decomposition and time-concentration curve fidelity.
Task 1.4 – Motion Correction:
Develop motion correction algorithms using 3D affine and deformable registration, supported by sharpness metrics and total variation regularization. Intra-scan motion will be addressed using entropy-based methods, tested by simulating motion in both digital and physical phantoms.
ii) Development and Optimization of a Reconstruction Algorithm for QDCE-DBT
WP2 focuses on building and refining the reconstruction algorithm to produce dynamic, iodine-only DBT maps from dual-energy data. It includes system characterization, improved regularization, faster reconstruction, and integration with other work packages.
Task 2.1: Detector Characterization
To ensure accurate reconstruction, the imaging detector will be thoroughly characterized. This includes measuring its response, homogeneity, ghosting, and lag. These properties will be incorporated into the reconstruction model to correct for non-linearities, especially important due to the longer scans and thicker detectors used in dual-energy imaging.
Task 2.2: Convergence Regularization
The reconstruction algorithm will be stabilized using multiple regularization strategies. These will incorporate prior knowledge about breast anatomy and time-series consistency. Because DBT is inherently anisotropic, tailored (likely anisotropic) regularizers will be designed to prioritize quantitative accuracy of the iodine maps, rather than just visual quality.
Task 2.3: Optimization and Acceleration
Reconstruction speed will be improved by optimizing algorithm steps and implementing them efficiently, particularly on GPUs. Strategic approximations will be introduced to speed up computation without compromising the accuracy of iodine quantification.
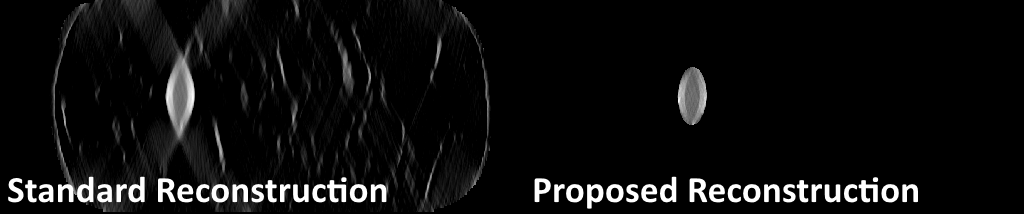
Figure 4: Our reconstruction method uses a deep learning-based segmentation to constrain the iodine component of the reconstruction only to the lesion area, limiting the artifacts and spread in the top-down direction seen in the standard reconstruction.
Task 2.4: Integration and Physical Testing
All algorithms from the previous tasks will be integrated into a seamless pipeline that processes data from input to final iodine maps. The entire system will then be tested on the physical breast phantom developed in WP1. Final adjustments will be made based on this testing to ensure high accuracy in iodine quantification over time.
iii) Develop and Test Deep Learning Networks for QDCE-DBT
WP3 focuses on using deep learning to finalize the QDCE-DBT imaging pipeline. It will correct x-ray scatter, estimate breast shape, and produce quantitative, time-resolved iodine-only DBT images.
Task 3.1: X-ray Scatter Correction
A modified U-Net will be developed to predict x-ray scatter maps in real-time for each DBT projection. The network will use inputs like projection angle and breast thickness, alongside a binary image of the breast shape. It will be trained on Monte Carlo-simulated data and integrated into the existing scatter correction workflow.
Task 3.2: Reconstruction Volume Constraining
Another U-Net will be trained to estimate the 3D shape of the breast from DBT projections, eliminating the need for a physical surface scan. Training data will include a large dataset of DBT images paired with optical scans. This will help constrain the reconstruction volume for improved image quality.
Task 3.3: Quantization of Iodine Map
The existing 2D iodine lesion segmentation network will be expanded to 3D. It will be trained on a diverse set of lesion types from MRI and CT data. Temporal information from early contrast phases will help separate iodine uptake from background parenchymal enhancement, improving segmentation accuracy, see Fig. 5.
Task 3.4: Alternative Iodine Quantization via LPD
An alternative approach will use a deep learning-based reconstruction method (Learned Primal-Dual algorithm) tailored for iodine map generation. This task-specific model will be trained on simulated data and synthetic breast shapes generated using variational autoencoders. It’s expected to be faster and more flexible, with strong potential for generalization to clinical data.
iv) Develop and Optimize Non-Contrast DE-DBT for Screening
WP4 focuses on adapting dual-energy digital breast tomosynthesis (DE-DBT) for non-contrast-based breast cancer screening. The aim is to differentiate cysts from solid masses using material decomposition, ultimately producing a "probability-of-cyst" score.
Task 4.1: DE-DBT Acquisition Optimization
Using digital phantoms and known compositions of cyst fluid and tumor tissue, this task will simulate and optimize DE image acquisition. The goal is to balance image quality and lesion characterization within standard screening dose limits. Both anatomic image quality (contrast and CNR) and lesion classification performance (AUC) will guide optimization.
Task 4.2: Spectral Reconstruction Regularization
A new regularization strategy will be developed to suit non-contrast DE-DBT. Unlike QDCE-DBT, this approach requires decomposing the breast image into two soft-tissue materials and comparing their proportions to known cyst and tumor values. This tailored regularization ensures accurate tissue composition estimates for diagnosis.
Task 4.3: Cyst Fluid Collection
Cyst fluid samples will be collected from 20 patients undergoing routine cyst aspiration during clinical procedures. Since the samples would otherwise be discarded and no personal data will be gathered, ethical approval is expected to be straightforward.
Task 4.4: Physical Phantom Testing
A modular breast phantom will be built to include real cyst fluid alongside solid masses. This phantom will enable DE-DBT imaging under realistic conditions. The results will help validate and fine-tune the software and evaluate the system’s effectiveness in distinguishing between cystic and solid lesions.

Figure 5. Top: Slice of a digital dynamic breast phantom. Bottom: different contrast enhancement curves from the different tissues.
Researchers: