Research
Deep Learning-based Reconstruction in CT Imaging
Deep learning reconstruction (DLR) is a new technology to reconstruct the CT projections into axial slices. This type of reconstruction allows to obtain reconstructed images in a short time and with low noise content, preserving at the same time the spatial resolution to the same extent as hybrid-iterative reconstruction methods in low dose settings.
DLR could be especially important in ultra-high-resolution (UHR) CT, a new scanner with detector element size about half the size of conventional multi-detector CT. In fact, the smaller detector element size of UHR-CT scanners results in inherent larger noise for the same detector dose (compared to traditional multi-detector CT), a fact that might limit their clinical applicability.
Therefore, in this project, the image quality deriving from DLR in UHR-CT is investigated, to assess whether such a novel reconstruction method can help reduce the image noise and, consequently, improve image quality.
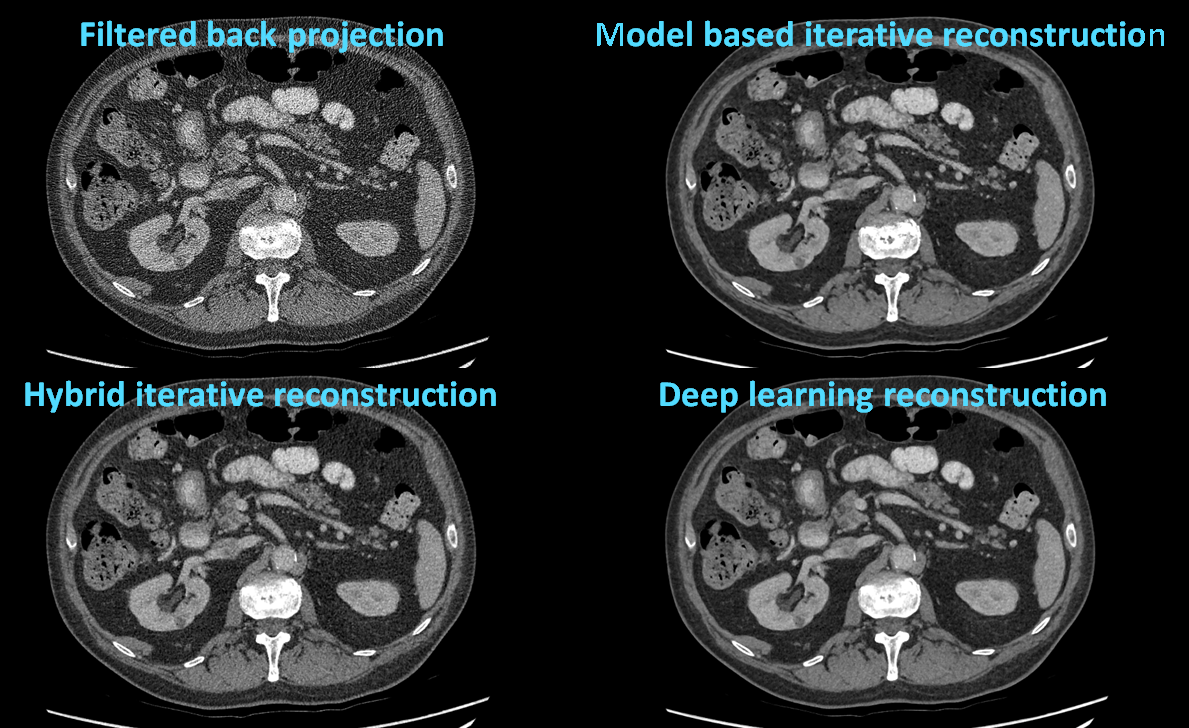
Abdominal CT reconstructed with four different reconstruction algorithms. Filtered backprojection and hybrid-iterative reconstruction produce more noise than model-based iterative reconstruction and deep-learning reconstruction. Deep learning reconstruction has a reconstruction time comparable to hybrid-iterative reconstruction.
Researchers: